Iatrogenic epidermoid tumor: late complication of lumbar puncture. Per H, Kumandaş S, Gümüş H. J Child Neurol. 2007 Mar;22(3):332-6. Department of Pediatric Neurology, Erciyes University, Medical Faculty, Kayseri, Turkey. Mail: huseyinper@yahoo.com
Intraspinal epidermoid tumors can be congenital and acquired. Acquired intraspinal epidermoid tumors are extremely rare. Epidermal elements are implanted into the arachnoid space by trauma, spinal anesthesia, surgery, bullet wounds, myelography, or lumbar puncture. Approximately 40% of acquired epidermoid tumors are considered a late complication of lumbar puncture. The authors report the case of an 8-year-old boy who presented with a 1-year history of back and hip pain and radiating pain to both thighs posterior. Lumbar puncture was performed in the neonatal intensive care unit to rule out meningitis in the patient's past medical history. The patient underwent total surgical excision of the epidermoid tumor. Pathologic examination revealed the diagnosis of epidermoid tumor.
--------------------------------------
Iatrogenic spinal epidermoid tumors. A late complication of spinal puncture. Reina MA, López-García A, Dittmann M, de Andrés JA, Blázquez MG. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 1996 Apr;43(4):142-6. Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital General de Móstoles, Madrid.
INTRODUCTION. Epidermoid tumors in the spinal canal are rare. Whether congenitally or iatrogenically caused, they form as the result of epidermal cells implanted within the spinal channel. Such implantation can occur during a variety of procedures and events such as bullet wounds, surgery, myelography or punctures for diagnosis, anesthesia or treatment. Although this complication is not discussed in books or journals on anesthesiology, we have found it mentioned in over 100 published cases reporting iatrogenically caused spinal epidermoid tumors.
ETIOPATHOGENESIS. Iatrogenic epidermoid tumors of the spine derive from the implantation of epidermal tissue transported inside the spinal canal during lumbar punctures without guidance or with inadequate guidance. There is ample evidence that such tumors are iatrogenic. All cases occur in patients with a history of lumbar puncture. They are rarely associated with congenital anomalies. They are extramedullary. They tend to develop near sites of earlier lumbar puncture, usually near the conus medullaris and the cauda equina. Iatrogenic epidermoid tumors of the spine have been reproduced experimentally in two studies in which autologous skin fragments were implanted in the spinal canal.
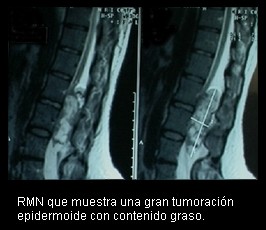
CLINICAL SIGNS. These tumors are well tolerated by patients for extended periods of time, ranging from 2 to 10 years. At the cauda equinus, tumors can grow slowly for long periods without signs of nerve compression. Symptoms are directly related to tumor size and site. All patients with tumors at the cauda equinus report severe pain radiating toward the roots of compressed nerves. Nuclear magnetic resonance makes it possible to detect the tumor without administration of intrathecal contrast. At present gadolinium-DTPA improves the image so that these tumors can be distinguished from other types. The prognosis for epidermoid tumors of the spine is good, as they are histologically benign. Treatment is always surgical.
CONCLUSION. Although the causal relation between epidermoid spinal tumors and lumbar puncture is well documented, anesthesiologists are not sufficiently aware of this possible complication. Between 1977 and 1995, 28 new cases were published. We believe that a deeper understanding of such rare complications will show us how to prevent them while providing appropriate use of epidural and subarachnoid anesthesia.
--------------------------------------
Iatrogenic spinal epidermoid tumor. A complication of spinal puncture in an adult. Park JC, Chung CK, Kim HJ. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2003 Sep;105(4):281-5. Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 28 Yoengeon-dong, Jongno-gu, 110-744, Seoul, South Korea. Mail: chungc@snu.ac.kr
A case of an intraspinal epidermoid tumor following a lumbar puncture (LP) is described. This tumor developed 5 years after a LP in a man aged 31 years. The majority of epidermoid tumors reported are late complications of spinal puncture during the early neonatal period. To the best of our knowledge, this case is the third oldest patient, whose symptoms presented relatively early after the initial LP. He was successfully treated by surgery. Pathologic diagnosis revealed an epidermoid cyst. The relation between LP and epidermoid tumor and the possible risk factors involved are discussed
Artículo: Bajar el documeto de la red. [Clic aquí]
